From $19.99
Transfer PAL MiniDV tape to digital format. (DVD, Blu-Ray, AVI, or any other format)
Canaan Media can transfer PAL MiniDV tapes or SECAM MiniDV tapes in a professional matter, to create a high quality long-term digital archive.
For NTSC MiniDVs, click here.
Definition from The Tech Terms Dictionary.
Most digital camcorders record video and audio on a MiniDV tape. A MiniDV tape that is 65 meters long can hold an incredible 11GB of data, or 80 minutes of digital video.
The small size of MiniDV tapes has helped camcorder manufacturers reduce the size of their video cameras significantly. Some consumer cameras that use MiniDV tapes are smaller than the size of your hand.
Definition from Wikipedia.
DV is a format for storing digital video. It was launched in 1995 with joint efforts of leading producers of video camera recorders
In 2005, DV was replaced with HDV, which used the same tape format in higher quality. Some cameras at the time had the ability to switch between DV and HDV recording modes.
DV was originally designed for recording onto magnetic tape. The tape is enclosed into four different sizes. (Small, medium, large and extra-large.) All DV cassettes use tape that is ¼ inch (6.35 mm) wide.
Small cassettes, also known as S-size or MiniDV cassettes, had been intended for amateur use, but have become accepted in professional productions as well. Each tape holds about 13 GB for one hour of video.
Medium or M-size cassettes are often called DVCPRO tapes. Panasonic video recorders that accept medium cassette can play back from and record to medium cassette in different flavors of DVCPRO format. They will also play small cassettes containing DV or DVCAM recording via an adapter.
Large or L-size cassettes are accepted by most standalone DV tape recorders and are used in many shoulder-mount camcorders. They are often called DVCAM tapes. Older Sony decks would not play large cassettes with DVCPRO recordings, but newer models can.
Definition from Wikipedia.
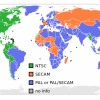
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) is a colour encoding system for analogue television used in broadcast television systems in most countries broadcasting at 625-line / 50 field (25 frame) per second (576i).
Definition from Wikipedia.
SECAM, also written SÉCAM (French for “Sequential Color with Memory”), is an analog color television system first used in France. A team led by Henri de France working at Compagnie Française de Télévision (later bought by Thomson, now Technicolor) invented SECAM. It is, historically, the first European color television standard. SECAM is in the process of being phased out and replaced by DVB.